Virtual evidence is a term used for a shortcut that allows for entering evidence for normally unobservable variables. A typical modeling practice in such cases is that we model such variables but next to them variables that are observable and can provide us with information about the unobservables. For example, we are typically unable to determine whether a disease is present or not but can model a medical test, which when observed will provide evidence for or against the disease. The test result is readily observable. Virtual evidence allows us for entering uncertain observation (in form of probability distribution over the possible states of the observation) directly into the normally unobservable variable.
Entering virtual observations/evidence is similar to entering evidence. The main difference is that instead of observing a state of a node, we enter a probability distribution over all states of the node. You may load the model VentureBN.xdsl created in Building a Bayesian network from the Example Networks folder. To start the virtual evidence dialog, right-click on the node in question (in the picture below, node Expert forecast) and choose Set Evidence, followed up by Virtual Evidence...
Alternatively, select the node in question and choose Set Evidence-Virtual Evidence... sub-menu from the Node Menu.
Yet another way is right-clicking on the updated icon of the node and using the context menu that pops up.
In each of these three cases, this invokes the following dialog for entering virtual evidence:
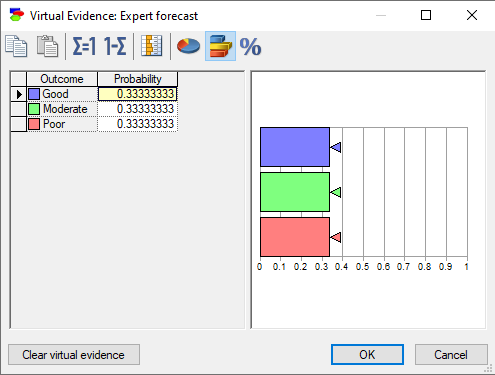
Virtual evidence can be entered numerically or graphically, using a probability wheel or a bar chart (pictured in the above screen shot). Keep in mind that virtual evidence is a probability distribution over the states of the observed variable and individual probabilities in the distribution have to add up to 1.0.
The internal implementation of virtual evidence in GeNIe is simple and equivalent to creating a temporary child node for each node with virtual evidence and populating its CPT with values based on the values entered as virtual evidence. The theoretical interpretation of this temporary node is that it provides uncertain information about its parent, which is what virtual evidence is about.
Retracting virtual evidence is identical to retracting evidence and has been described in section Entering and retracting evidence.
To enter different evidence instead of retracting evidence altogether, invoke the Virtual Evidence Dialog and set different evidence.