You can load the contents of a data set from a text file by calling DSL_dataset::ReadFile. For the illustration purposes, let us assume that we have a comma separated text file with the following data:
VarA,VarB,VarC
44.225,3,StateZ
26.913,0,StateY
24.379,2,*
*,3,StateX
76.681,*,StateZ
44.702,1,StateX
After the DSL_dataset::ReadFile call, the data set will be structured as below:
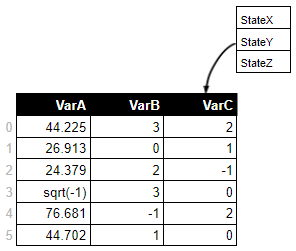
•variable VarA is continuous. The value missing in the fourth record was replaced by sqrt(-1).
•variable VarB is discrete. The value missing in the fifth record was replaced by -1.
•variable VarC is also discrete, and has the string labels associated with its integer values. The value missing in the third record was replaced by -1.
You can fine-tune the parsing by passing a DSL_datasetParseParams structure to ReadFile. The following code should be used if the data file has no header line with the names of the columns, missing values are marked by a "N/A" string and missing values in discrete columns should be replaced by 999:
DSL_dataset ds;
DSL_datasetParseParams params;
params.columdIdsPresent = false;
params.missingValueToken = "N/A";
params.missingInt = 999;
int res = ds.ReadFile("datafile.txt", ¶ms);
To write the contents of the data set to a text file, use DSL_dataset::WriteFile. You can customize the field separator, the missing value marker, etc. by passing a DSL_datasetWriteParams structure to WriteFile. The code snippet below writes a comma-separated file, which includes a header line with column names and uses "(none)" as a marker for missing values:
DSL_dataset ds;
// create or load dataset here
DSL_datasetWriteParams params;
params.columdIdsPresent = true;
params.missingValueToken = "(none)";
params.separator = ',';
int res = ds.WriteFile("datafile.csv", ¶ms);