The Most probable explanation (MPE) algorithm is a special case of the Annealed MAP algorithm (Yuan et al., 2004) and it solves the problem of finding the most likely configuration of values of all model nodes (those nodes that have been observed already have their most probable values) rather than a selected subset of nodes. The Annealed MAP algorithm is approximate and solves the problem by means of an approximate optimization procedure called simulated annealing.
To invoke the algorithm dialog, select Most probable explanation from the Network Menu
MPE dialog
The MPE dialog that appears shows the results of the calculation and two window panes.
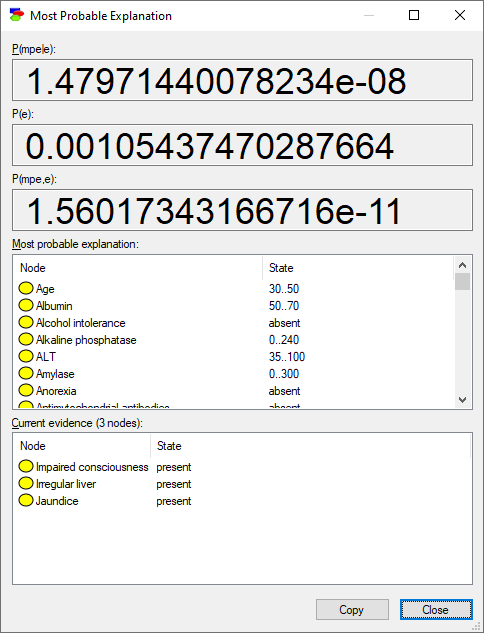
The lower window pane contains Current evidence nodes and their States. In this case, there are three observed evidence nodes.
The middle pane contains all other model nodes, i.e., all nodes in the current network that have not been observed along with their most probable states.
Algorithm results
The MPE algorithm finds the maximum a posteriori probability assignment of states to the model variable and calculates the following three probabilities:
•P(MPE|E): The probability of the MPE assignment given the set of evidence
•P(E): The probability of evidence
•P(MPE,E): The joint probability of MPE assignment and the evidence
We can read from the results that the most likely combination of states of the nodes (shown in the middle pane) has the probability of P(MPE|E)=0.1.4797 10-8.
Pressing Copy copies the most important results to the clipboard. The results can be pasted into a different program. The paste operation in the above example gives the following result:
P(mpe|e)=1.47971440078234e-08
P(e)=0.00105437470287664
P(mpe,e)=1.56017343166716e-11
Most probable explanation:
Age 30..50
Albumin 50..70
Alcohol intolerance absent
Alkaline phosphatase 0..240
ALT 35..100
Amylase 0..300
Anorexia absent
Antimytochondrial antibodies absent
Ascites present
AST 40..150
Blood urea 0..40
Carcinoma absent
Choledocholithotomy absent
Chronic hepatitis absent
Cirrhosis absent
Diabetes absent
Edema absent
Enlarged spleen absent
ESR 0..14
Fat intolerance absent
Fatigue present
Flatulence absent
Functional hyperbilirubinemia absent
Gallstones absent
GGTP 0..10
Haemorrhagie diathesis absent
Hepatalgia absent
Hepatic encephalopathy absent
Hepatic fibrosis absent
Hepatic steatosis absent
Hepatomegaly present
Hepatotoxic medications absent
History of alcohol abuse absent
History of hospitalization absent
History of transfusion absent
History of viral hepatitis absent
Increased liver density absent
Injections in the past absent
INR 70..110
Irregular liver edge absent
Itching absent
Joints swelling absent
LE cells absent
Liver palms absent
Musculo-skeletal pain absent
Nausea absent
Obesity absent
Pain in right upper quadrant absent
PBC absent
Platelet count 150..300
Presence of antibodies to HBcAg in blood absent
Presence of antibodies to HBsAg in blood absent
Presence of antibodies to HCV in blood absent
Presence of hepatitis B antigen in blood absent
Presence of hepatitis B surface antigen in blood absent
Pressure in right upper quadrant absent
Reactive hepatitis absent
Sex female
Surgery in the past absent
Total bilirubin 0..2
Total cholesterol 0..240
Total proteins 6..10
Total triglycerides 0..2
Toxic hepatitis absent
Upper abdominal pain absent
Vascular spiders absent
Yellowing of the skin absent
Evidence:
Impaired consciousness present
Irregular liver present
Jaundice present
Pressing Close closes the Most Probable Explanation dialog.
Parameters
The MPE algorithm is a special case of the Annealed MAP algorithm, which has seven parameters that can be fine-tuned to obtain better results. To change the default values of these parameters, please invoke the Annealed MAP algorithm.